Getting started with Graph Part 1
Tags: graph java implementation

Graph are data structures made of vertices & edges. There are lots of interesting problems that can be solved using graphs. Part 1 covers the basic for creating a template for graph data structure.
First we need to create a vertex. A vertex is a fundamental unit of graph. A graph is a set of points (vertices) connected by lines (edges).
 |
Create a vertex
First we need to create a vertex. A vertex is a fundamental unit of graph. A graph is a set of points (vertices) connected by lines (edges).
class Vertex {
String label;
public Vertex(String label) {
this.label = label;
}
}
Represent a graph
We need a data structure to represent our graph. We have two choices
- Adjacency Matrix
- Adjacency List
So we have a graph like below
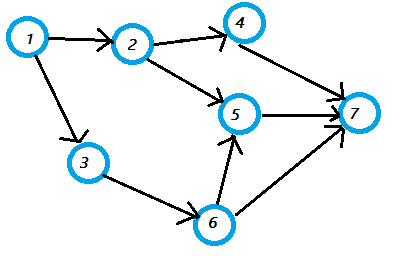 |
Using Adjaceny matrix
1 means edge between two vertex where as 0 means no edge
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Using Adjacency List (we'll be using this for efficiency)
Here each vertex correspond to a linked list of outgoing edges
| 1 → 2, 3 |
| 2 → 4, 5 |
| 3 → 6 |
| 4 → 7 |
| 5 → 7 |
| 6 → 5 , 7 |
| 7 |
class Vertex {
String label;
public Vertex(String label) {
this.label = label;
}
}
class Graph {
//adjacency list
private Map<Vertex, List<Vertex>> adjList = new HashMap<>();
}
Add lots of vertex (or vertices)
We now need to add add vertex (if it doesn't exist) to our graph using method addVertex
class Vertex {
String label;
public Vertex(String label) {
this.label = label;
}
public boolean hasKey(String label) {
return label.equals(this.label);
}
}
class Graph {
//adjacency list
private Map<Vertex, List<Vertex>> adjList = new HashMap<>();
public void addVertex(String label) {
for (Map.Entry<Vertex, List<Vertex>> entry : adjList.entrySet()) {
Vertex temp = entry.getKey();
if (temp.hasKey(label)) {
return;
}
}
adjList.put(new Vertex(label), new ArrayList<>());
}
}
Add Edges
We need to add edges between two vertex (if not already existing)
class Vertex {
...
public String getKey() { return this.label; }
}
class Graph {
...
public void addEdge(String label1, String label2) {
Vertex v1 = new Vertex(label1);
Vertex v2 = new Vertex(label2);
for (Map.Entry<Vertex, List<Vertex>> entry : adjList.entrySet()) {
Vertex temp = entry.getKey();
if (temp.hasKey(label1)) {
adjList.get(temp).add(new Vertex(label2));
}
}
}
}
Is that it?
Yup. It's a basic template for a simple graph. Below is the full code
class Vertex {
String label;
public Vertex(String label) {
this.label = label;
}
public boolean hasKey(String label) {
return label.equals(this.label);
}
public String getKey() { return this.label; }
}
class Graph {
//adjacency list
private Map<Vertex, List<Vertex>> adjList = new HashMap<>();
public void addVertex(String label) {
for (Map.Entry<Vertex, List<Vertex>> entry : adjList.entrySet()) {
Vertex temp = entry.getKey();
if (temp.hasKey(label)) {
return;
}
}
adjList.put(new Vertex(label), new ArrayList<>());
}
public void addEdge(String label1, String label2) {
Vertex v1 = new Vertex(label1);
Vertex v2 = new Vertex(label2);
for (Map.Entry<Vertex, List<Vertex>> entry : adjList.entrySet()) {
Vertex temp = entry.getKey();
if (temp.hasKey(label1)) {
adjList.get(temp).add(new Vertex(label2));
}
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph();
//add vertices
graph.addVertex("1");
graph.addVertex("2");
graph.addVertex("3");
graph.addVertex("4");
graph.addVertex("5");
graph.addVertex("6");
graph.addVertex("7");
//add edges
graph.addEdge("1", "2");
graph.addEdge("1", "3");
graph.addEdge("2", "4");
graph.addEdge("2", "4");
graph.addEdge("2", "5");
graph.addEdge("3", "6");
graph.addEdge("4", "7");
graph.addEdge("5", "7");
graph.addEdge("6", "5");
graph.addEdge("6", "7");
}
}
Conculsion
It concludes Part 1 of graph series. Later series will cover much more operations on graph.
comments powered by Disqus
